#Unix environment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

Charles A. Csuri Faces (1989)
352 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’m not a wizard, but I am reading a book with a sentence that starts with “If whence is SEEK_END”
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
KDE Plasma 6 released!
New major version of the best computer desktop environment ever is finally here. Check out the new overview, improved colour management, a cleaner theme, more effects, better overall performance, and much more.
#linux#linux desktop#unix#bsd#kde#kde plasma#software#opensource#open source#freesoftware#free software#computers#apps#applications#desktop environment#desktop#technology#plasma6#Plasma 6
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
I don't think people realize how absolutely wild Linux is.
Here we have an Operating system that now has 100 different varieties, all of them with their own little features and markets that are also so customizable that you can literally choose what desktop environment you want. Alongside that it is the OS of choice for Supercomputers, most Web servers, and even tiny little toy computers that hackers and gadget makers use. It is the Operating System running on most of the world's smartphones. That's right. Android is a version of Linux.
It can run on literally anything up to and including a potato, and as of now desktop Linux Distros like Ubuntu and Mint are so easily to use and user friendly that technological novices can use them. This Operating system has had App stores since the 90s.
Oh, and what's more, this operating system was fuckin' built by volunteers and users alongside businesses and universities because they needed an all purpose operating system so they built one themselves and released it for free. If you know how to, you can add to this.
Oh, and it's founder wasn't some corporate hotshot. It's an introverted Swedish-speaking Finn who, while he was a student, started making his own Operating system after playing around with someone else's OS. He was going to call it Freax but the guy he got server space from named the folder of his project "Linux" (Linus Unix) and the name stuck. He operates this project from his Home office which is painted in a colour used in asylums. Man's so fucking introverted he developed the world's biggest code repo, Git, so he didn't have to deal with drama and email.
Steam adopted it meaning a LOT of games now natively run in Linux and what cannot be run natively can be adapted to run. It's now the OS used on their consoles (Steam Deck) and to this, a lot of people have found games run better on Linux than on Windows. More computers run Steam on Linux than MacOS.
On top of that the Arctic World Archive (basically the Svalbard Seed bank, but for Data) have this OS saved in their databanks so if the world ends the survivors are going to be using it.
On top of this? It's Free! No "Freemium" bullshit, no "pay to unlock" shit, no licenses, no tracking or data harvesting. If you have an old laptop that still works and a 16GB USB drive, you can go get it and install it and have a functioning computer because it uses less fucking resources than Windows. Got a shit PC? Linux Mint XFCE or Xubuntu is lightweight af. This shit is stopping eWaste.
What's more, it doesn't even scrimp on style. KDE, XFCE, Gnome, Cinnamon, all look pretty and are functional and there's even a load of people who try make their installs look pretty AF as a hobby called "ricing" with a subreddit (/r/unixporn) dedicated to it.
Linux is fucking wild.
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
Who Broke the Internet? Part III

I'm on a 20+ city book tour for my new novel PICKS AND SHOVELS. Catch me in PDX on Jun 20 at BARNES AND NOBLE with BUNNIE HUANG. After that, it's LONDON (Jul 1) and MANCHESTER (Jul 2).

Episode 3 of "Understood: Who Broke the Internet?" (my new CBC podcast about enshittification) just dropped. It's called "In God We Antitrust," and it's great:
https://www.cbc.ca/listen/cbc-podcasts/1353-the-naked-emperor/episode/16147052-in-god-we-antitrust
The thesis of this four-part series is pretty straightforward: the enshittification of the internet was the result of an enshittogenic policy environment. Platforms always had the technical means to scam us and abuse us. Tech founders and investors always included a cohort of scumbags who would trade our happiness and wellbeing for their profits. What changed was the consequences of giving in to those impulses. When Google took off, its founders' mantra was "competition is just a click away." If someone built a better search engine, users could delete their google.com bookmarks, just like they did to their altavista.com bookmarks when Google showed up.
Policymakers – not technologists or VCs – changed the environment so that this wasn't true anymore:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/05/08/who-broke-the-internet/#bruce-lehman
In last week's episode, we told the story of Bruce Lehman, the Clinton administration's Copyright Czar, who swindled the US government into passing a law that made it illegal to mod, hack, reverse-engineer or otherwise improve on an existing technology:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/05/13/ctrl-ctrl-ctrl/#free-dmitry
This neutralized a powerful anti-enshittificatory force: interoperability. All digital tech is born interoperable, because of the intrinsic characteristics of computers, their flexibility. This means that tech is inherently enshittification-resistant. When a company enshittifies its products or services, its beleaguered users and suppliers don't have to wait for a regulator to punish it. They don't have to wait for a competitor to challenge it.
Interoperable tools – ad-blockers, privacy blockers, alternative clients, mods, plugins, firmware patches and other hacks – offer immediate, profound relief from enshittification. Every ten foot pile of shit that a tech company drops into your life can be met with an eleven foot ladder of disenshittifying, interoperable technology.
That's why Lehman's successful attack on tinkering was so devastating. Before Lehman, tech had achieved a kind of pro-user equilibrium: every time a company made its products worse, they had to confront a thousand guerrilla technologists who unilaterally unfucked things: third party printer ink, file-format compatibility, protocol compatibility, all the way up to Unix, a massive operating system that was painstakingly re-created, piece by piece, in free software.
Lehman offered would-be enshittifiers a way to shift this equilibrium to full enshittification: just stick a digital lock on your product. It didn't even matter if the lock worked – under Lehman's anticircumvention law, tampering with a lock, even talking about weaknesses in a lock, became a literal felony, punishable by a five-year prison sentence and a $500K fine. Lehman's law was an offer no tech boss would refuse, and enshittification ate the world.
But Lehman's not the only policymaker who was warned about the consequences of his terrible plans, who ignored the warnings, and who disclaims any responsibility for the shitty world that followed. Long before Lehman's assault on tech policy, another group of lawyers and economists laid waste to competition policy.
In the 1960s and 1970s, a group of Chicago School economists conceived of an absurd new way to interpret competition law, which they called "the consumer welfare standard." Under this standard, the job of competition policy was to encourage monopolies to form, on the grounds that monopolies were "efficient" and would lower prices for "consumers."
The chief proponent of this standard was Robert Bork, a virulent racist whose most significant claim to fame was that he was the only government lawyer willing to help Richard Nixon illegally fire officials who wouldn't turn a blind eye to his crimes. Bork's long record of unethical behavior and scorching bigotry came back to bite him in the ass when Ronald Reagan tried to seat him on the Supreme Court, during a confirmation hearing that Bork screwed up so badly that even today, we use "borked" as a synonym for anything that is utterly fucked.
But Bork's real legacy was as a pro-monopoly propagandist, whose work helped shift how judges, government enforcers, and economists viewed antitrust law. Bork approached the text of America's antitrust laws, like the Sherman Act and the Clayton Act, with the same techniques as a Qanon follower addressing a Q "drop," applying gnostic techniques to find in these laws mystical coded language that – he asserted – meant that Congress had intended for America's anti-monopoly laws to actually support monopolies.
In episode three, we explore Bork's legacy, and how it led to what Tom Eastman calls the internet of "five giant websites, each filled with screenshots of the other four." We got great interviews and old tape for this one, including Michael Wiesel, a Canadian soap-maker who created a bestselling line of nontoxic lip-balm kits for kids, only to have Amazon shaft him by underselling him with his own product.
But the most interesting interview was with Lina Khan, the generational talent who became the youngest-ever FTC chair under Joe Biden, and launched an all-out assault on American monopolies and their vile depredations:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/14/making-good-trouble/#the-peoples-champion
Khan's extraordinary rise to power starts with a law review paper she wrote in her third year at Yale, "Amazon's Antitrust Paradox," which became the first viral law review article in history:
https://www.yalelawjournal.org/note/amazons-antitrust-paradox
"Amazon's Antitrust Paradox" was a stinging rebuke to Bork and his theories, using Amazon's documented behavior to show that after Amazon used its monopoly power to lower prices and drive rivals out of the market, it subsequently raised prices. And, contrary to Bork's theories, those new, high prices didn't conjure up new rivals who would enter the market with lower prices again, eager to steal Amazon's customers away. Instead, Amazon's demonstrated willingness to cross-subsidize divisions gigantic losses to destroy any competitor with below-cost pricing created a "kill zone" of businesses adjacent to the giant's core enterprise that no one dared enter:
https://www.thebignewsletter.com/p/how-biden-can-clean-up-obamas-big
The clarity of Khan's writing, combined with her careful research and devastating conclusions dragged a vast crowd of people who'd never paid much attention to antitrust – including me! – into the fray. No wonder that four years later, she was appointed to serve as the head of the FTC, making her the most powerful consumer rights regulator in the world.
We live in an age of monopolies, with cartels dominating every part of our lives, acting as "autocrats of trade" and "kings over the necessaries of life," the corporate dictators that Senator John Sherman warned about when he was stumping for the 1890 Sherman Act, America's first antitrust law:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/20/we-should-not-endure-a-king/
Bork and his co-religionists created this age. They're the reason we live in world where we have to get our "necessaries of life" from a cartel, a duopoly or a monopoly. It's not because the great forces of history transformed the economy – it's because of these dickheads:
https://www.openmarketsinstitute.org/learn/monopoly-by-the-numbers
This episode of "Understood: Who Borked the Internet?" draws a straight line from those economists and their ideas to the world we live in today. It sets up the final episode, next week's "Kick 'Em in the Dongle," which charts a course for us to escape from the hellscape created by Bork, Lehman, and their toadies and trolls.
You can get "Understood: Who Broke the Internet?" in any podcast app, even the seriously enshittified ones (which, let's be real here, is most of them). Here's a direct link to the RSS:
https://www.cbc.ca/podcasting/includes/nakedemperor.xml

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/05/19/khan-thought/#they-were-warned
#pluralistic#enshittification#podcasts#understood#cbc#cbc understood#antitrust#trustbusting#robert bork#oligarchy#amazon#lina khan#ftc#amazons antitrust paradox
167 notes
·
View notes
Text
On Celebrating Errors

Isn't it beautiful? The lovely formatted tables of register and stack contents, the trace of function addresses and parameters, the error message ... it's the most beautiful kernel panic I have ever seen.
Why on earth would I be so excited to see a computer crash? What could possibly be beautiful about a kernel panic?
This kernel panic is well-earned. I fought hard to get it.
This kernel panic came from a current NetBSD kernel, freshly compiled and running on Wrap030, my 68030 homebrew computer. It is the result of hours upon hours of work reading through existing code, scattered documentation and notes, writing and rewriting, and endless compiling.
And it's just the start.
As I've said before, a goal of this project has always been to build something capable of running some kind of Unix-like operating system. Now that I finally have all the necessary pieces of hardware, plus a good bootloader in ROM, it's time to give it a shot. I'm not that great with this type of programming, but I have been getting better. I might just be able to brute force my way through hacking together something functional.
It is hard.
There is some documentation available. The man(9) pages are useful, and NetBSD has a great guide to setting up the build environment for cross-compiling the kernel. There are some published papers on what some people went through to port NetBSD to this system or that. But there's nothing that really explains what all these source code files are, and which parts really need to be modified to run on a different system.
I had a few false starts, but ultimately found an existing 68k architecture, cesfic, which was a bare minimum configuration that could serve well as a foundation for my purposes. I copied the cesfic source directory, changed all instances of the name to wrap030, made sure it still compiled, then set about removing everything that I didn't need. It still compiled, so now it's was time to add in what I did need.
... how ... do I ... ?
This is where things get overwhelming very quickly. There is documentation on the core functions required for a new driver, there's documentation on the autoconf system that attaches drivers to devices in the tree, and there's plenty of drivers already to reference. But where to start?
I started by trying to add the com driver for the 16550 UARTs I'm using. It doesn't compile because I'm missing dependencies. The missing functions are missing because of a breaking change to bus.h at some point; the com driver expects the new format but the cesfic port still uses the old. So I needed to pull in the missing functions from another m68k arch. Which then required more missing functions and headers to be pulled in. Eventually it compiled without error again, but that doesn't mean it will actually run. I still needed to add support for my new programmable timer, customize the startup process, update hardware addresses, make sure it was targeting 68030 instead of 68040 ...
So many parts and pieces that need to be updated. Each one requiring searching for the original function or variable declaration to confirm expected types or implementation, then searching for existing usages to figure out what it needs ... which then requires searching for more functions and variable types.
But I got something that at least appeared to have all the right parts and compiled without error. It was time to throw it on a disk, load it up, and see what happened.
Nothing happened, of course. It crashed immediately.
I have no debugging workflow I can rely on here, and at this stage there isn't even a kernel console yet. All I could do was add little print macros to the locore startup code and see where it failed. Guess, test, and revise.
I spent a week debugging the MMU initialization. If the MMU isn't properly configured, everything comes to an abrupt halt. Ultimately, I replaced the cesfic machine-specific initialization code and pmap bootstrapping code with functions from yet another m68k arch. And spent another day debugging before realizing I had missed a section that had comments suggesting it wasn't for the 68030 CPU, but turned out to be critical for operation of kernel memory allocation.
Until this point, I was able to rely on the low-level exception handling built into my bootloader if my code caused a CPU exception. But with the MMU working, that code was no longer mapped.
So then came another few hours learning how to create a minimal early console driver. An early console is used by the kernel prior to the real console getting initialized. In this case, I'm using the MC6850 on my mainboard for the early console, since that's what my bootloader uses. And finally the kernel was able to speak for itself.
It printed its own panic.
The first thing the kernel does is initialize the console. Which requires that com driver and all the machine-specific code I had to write. The kernel is failing at its step #1.
But at least it can tell me that now. And given all the work necessary to get to this point, that kernel panic data printing to the terminal is absolutely beautiful.
#troubleshooting#coding#os development#netbsd#homebrew computer#homebrew computing#mc68030#motorola 68k#motorola 68030#debugging#wrap030#retro computing
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
Welcome to my blog!!
I'm @sunos-official, a blog to celebrate the wonders of the BSD (and later SVR4)-based Unix from Sun Microsystems in all of its iterations (although this blog will primarily focus on versions up to and including Solaris 9, with some appearances of Solaris 10).
I'll be working on populating the queue with fun Sun Microsystems-related goodness. In the mean time, enjoy some SunOS user interfaces!!

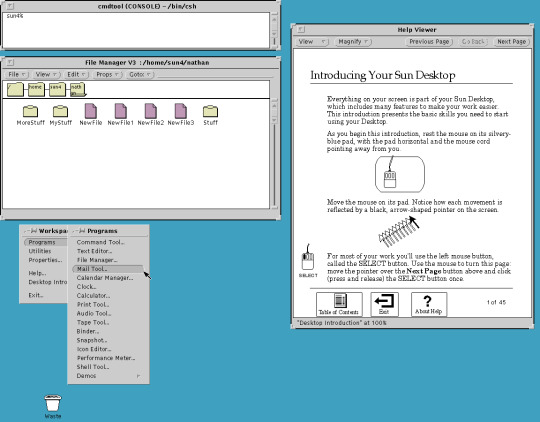
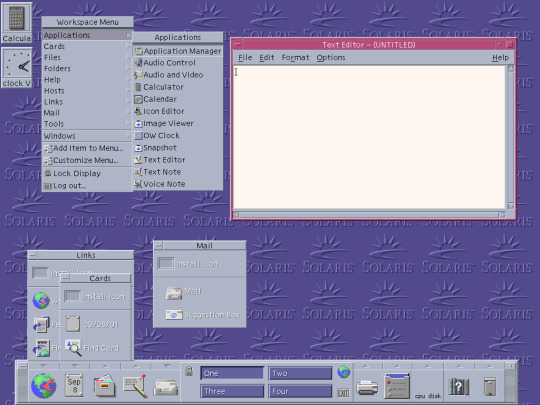
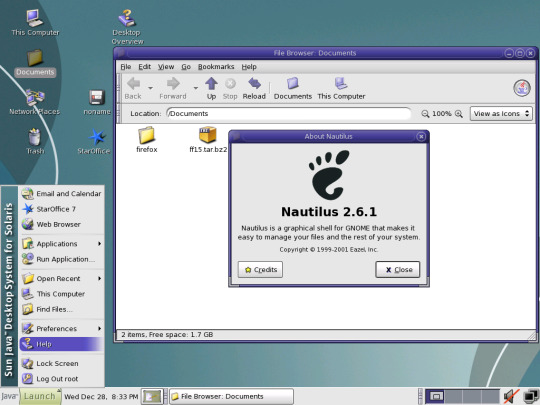
Pictured, clockwise from top left are:
SunView, SunOS 4
OpenWindows 3, SunOS 4
Common Desktop Environment, Solaris 8
Java Desktop System, Solaris 10
#unix#sun microsystems#retro computers#retro computing#old computers#operating system#solaris#sunos#vintage computer#sparc
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi!
Felt that I should make a *-official of my own, and this is it! I've been learning C, and having a blast discovering linux (And Unix-based in general) systems, so this seemed like an obvious choice!
Probably going to be posting some updates on how the whole c thing is going along with all the usual official stuff. Also very interested in interface design, so I'm trying out all the environments.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
1d. First Day at the Lab - Outliers
Name: Ren
Day: 1
Funds: $ 100
Today is my first day working at Ar Leith Labs - I can't believe I finally landed a job!
To be honest, I didn't look too deeply into what they do at Ar Leith Labs - I basically sent my curriculum to every neuroscience research lab that was hiring. Now that I'm here, I can't even find a pamphlet explaining the research in detail.
Ok, I'll be professional and go introduce myself to my coworkers now; either them or the PI can tell me more about the job.
---
There are only two other research assistants in my group: Leanne and Perry; neither of them seems to be the chatty type, at least not with me. I was looking forward to meeting my PI, but Leanne told me that she has never shown her face around here.
Right then we heard the PI speak; it felt as if she was standing right next to us. This lab must have a pretty technologically advanced speaker system!
The PI's voice welcomed me and introduced herself as C.N, just her initials; she invited me to get acquainted with the lab environment, and help my coworkers out with anything they might need.
I found it a little odd that she's not meeting us in person, but maybe there's an excellent reason for it. I don't want to pry, especially not on my first day.
Nobody was available to give me a tour - lots of work to do, which is fair - so I walked around the lab by myself, studying the equipment. I didn't recognize any of the machines, except for the obvious desktop computer in the corner. That one even looks a little old, in contrast with the rest of the devices.
Leanne noticed me looking at the computer and asked if I know how to code; heck yeah I do, I took a few classes and I'm pretty ok at it! So she asked me to write a bit of code to generate graph data for her latest research data. It's strange that they don't have software for that already, but I decided to avoid asking any questions.
I took this opportunity to look over the data, hoping it would clarify what kind of research we're supposed to do here, but I couldn't make heads or tails of it. Oh, well.
I couldn't recognize the OS the computer is running either, but it seemed loosely based on Unix. I was making good progress until I started testing my code; I got the error "Unable to find or open '/Brain/TemporalLobe/Hippocampus/MISTAKE.png'". I'm 100% sure I never referenced this file, and what a bizarre name!
I immediately thought this must be a prank - Leanne and Perry must have planned this as a funny welcome for me. I resolved to laugh and tell them it was a cool prank; that would show them I'm chill.
Unfortunately, they kept insisting they didn't know what I was talking about. They looked annoyed, so I assume they were being truthful. Alright, time to debug.
A quick search of the codebase and external libraries for the file path in the error message yielded no results. I tried looking just for "Mistake.png" and got nothing once again.
Interestingly enough, though, "Ren/Brain/" exists, except there's only a "temp" folder in there. Maybe I don't have the right access levels to see other folders? There doesn't seem to be a root user either.
I bothered Leanne and Perry to see whether they have access to the other folders - they don't, but they have their own users on this machine, with their own "/Brain/" folders. Also, my code wasn't available to them. They said the users were already set up for them when they joined, just like mine; IT support must be incredible around here.
In the end I decided to share the code with Leanne's user, in the off chance it would work for her. It did, just like I hoped, and Leanne got her graph.
I don't fully understand, but... great. Maybe I should talk to the IT support people, or take a few more coding classes.
---
The rest of the day was spent on boring menial tasks.
I bet my coworkers think I'm more trouble than I'm helpful, but hey - they'll change their minds, soon enough. After all, I didn't graduate top of my class just to be ignored at my job.
Luckily, at least C.N. already sees potential in me: before I left for the day, she said tomorrow I'll be tabling at an event called "The Gathering"! My first table, and on day 2? I can't wait!
I forgot to ask for the address, but I bet I can find all the info I need online. I'm obviously being tested, and I will show initiative, dependability, and bring a ton of new participants for the study!
--------------------
This is a playthrough of a solo TTRPG called "Outliers", by Sam Leigh, @goblinmixtape.
You can check it out on itch.io: https://far-horizons-co-op.itch.io/outliers
#indie ttrpg#itch.io#journal entry#journaling#playthrough#ttrpg#solo games#solo ttrpg#tabletop role playing game#tabletop roleplaying#outliers#lab notes#outliers ttrpg
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
list of things external to the Linux or GNU projects that you have to learn to some extent to get a comfortable multimedia desktop and programming environment for a project of significant size: X11, Wayland, Gtk, Qt, Terminal Emulators, Pipewire, PulseAudio, XDG Protocols (Open, Desktop portals, Desktop entries), NetworkManager/iwd/wpa_supplicant, GRUB, Systemd, Cmake, Wine, Clang, a decent text editor (meaning: not vi or nano). all of these have completely different configuration standards and interfaces
list of things you need external to the 9front distribution of plan 9 to get a comfortable multimedia desktop and programming environment for a project of significant size: netsurf if you really need a browser with css support? rio themes are still contained in a patch and not installed by default but they're on the contrib 9p share and really easy to get. you can get an ext4 filesystem server on contrib too, to get files to and from a unix without booting a second machine. video playback is possible with treason, on contrib. all of it is spoken to with launch flags, file descriptors (stdin/out), pipes, and filesystem reads and writes
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Building Your Own Operating System: A Beginner’s Guide
An operating system (OS) is an essential component of computer systems, serving as an interface between hardware and software. It manages system resources, provides services to users and applications, and ensures efficient execution of processes. Without an OS, users would have to manually manage hardware resources, making computing impractical for everyday use.

Lightweight operating system for old laptops
Functions of an Operating System
Operating systems perform several crucial functions to maintain system stability and usability. These functions include:
1. Process Management
The OS allocates resources to processes and ensures fair execution while preventing conflicts. It employs algorithms like First-Come-First-Serve (FCFS), Round Robin, and Shortest Job Next (SJN) to optimize CPU utilization and maintain system responsiveness.
2. Memory Management
The OS tracks memory usage and prevents memory leaks by implementing techniques such as paging, segmentation, and virtual memory. These mechanisms enable multitasking and improve overall system performance.
3. File System Management
It provides mechanisms for reading, writing, and deleting files while maintaining security through permissions and access control. File systems such as NTFS, FAT32, and ext4 are widely used across different operating systems.
4. Device Management
The OS provides device drivers to facilitate interaction with hardware components like printers, keyboards, and network adapters. It ensures smooth data exchange and resource allocation for input/output (I/O) operations.
5. Security and Access Control
It enforces authentication, authorization, and encryption mechanisms to protect user data and system integrity. Modern OSs incorporate features like firewalls, anti-malware tools, and secure boot processes to prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats.
6. User Interface
CLI-based systems, such as Linux terminals, provide direct access to system commands, while GUI-based systems, such as Windows and macOS, offer intuitive navigation through icons and menus.
Types of Operating Systems
Operating systems come in various forms, each designed to cater to specific computing needs. Some common types include:
1. Batch Operating System
These systems were widely used in early computing environments for tasks like payroll processing and scientific computations.
2. Multi-User Operating System
It ensures fair resource allocation and prevents conflicts between users. Examples include UNIX and Windows Server.
3. Real-Time Operating System (RTOS)
RTOS is designed for time-sensitive applications, where processing must occur within strict deadlines. It is used in embedded systems, medical devices, and industrial automation. Examples include VxWorks and FreeRTOS.
4 Mobile Operating System
Mobile OSs are tailored for smartphones and tablets, offering touchscreen interfaces and app ecosystems.
5 Distributed Operating System
Distributed OS manages multiple computers as a single system, enabling resource sharing and parallel processing. It is used in cloud computing and supercomputing environments. Examples include Google’s Fuchsia and Amoeba.
Popular Operating Systems
Several operating systems dominate the computing landscape, each catering to specific user needs and hardware platforms.
1. Microsoft Windows
It is popular among home users, businesses, and gamers. Windows 10 and 11 are the latest versions, offering improved performance, security, and compatibility.
2. macOS
macOS is Apple’s proprietary OS designed for Mac computers. It provides a seamless experience with Apple hardware and software, featuring robust security and high-end multimedia capabilities.
3. Linux
Linux is an open-source OS favored by developers, system administrators, and security professionals. It offers various distributions, including Ubuntu, Fedora, and Debian, each catering to different user preferences.
4. Android
It is based on the Linux kernel and supports a vast ecosystem of applications.
5. iOS
iOS is Apple’s mobile OS, known for its smooth performance, security, and exclusive app ecosystem. It powers iPhones and iPads, offering seamless integration with other Apple devices.
Future of Operating Systems
The future of operating systems is shaped by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and edge computing. Some key trends include:
1. AI-Driven OS Enhancements
AI-powered features, such as voice assistants and predictive automation, are becoming integral to modern OSs. AI helps optimize performance, enhance security, and personalize user experiences.
2. Cloud-Based Operating Systems
Cloud OSs enable users to access applications and data remotely. Chrome OS is an example of a cloud-centric OS that relies on internet connectivity for most functions.
3. Edge Computing Integration
With the rise of IoT devices, edge computing is gaining importance. Future OSs will focus on decentralized computing, reducing latency and improving real-time processing.
4. Increased Focus on Security
Cyber threats continue to evolve, prompting OS developers to implement advanced security measures such as zero-trust architectures, multi-factor authentication, and blockchain-based security.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
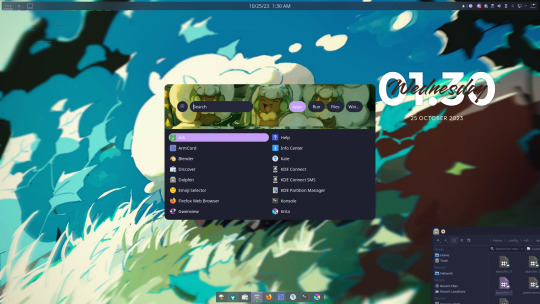
I've been moving over to Linux (KDE) and it's honestly been a great experience.
It's been years since I touched any unix system but I've always known what I was getting into. I am quite surprised how far Linux as a whole has come since then especially for desktop environments (it's always been fantastic for servers and specialized systems)
Installing it was stupid easy.
Setting things up took more work than what you might expect on windows (cloning and building git repos with dependencies via terminal as opposed to one click installers) but the tradeoff is things don't come with bloat, are tweaked specifically for my machine and system, I know exactly what I installed, and it runs better than windows in many cases. Overall a happy camper there.
KDE is quite something else as well. Lots of cool features you could either only dream of or have to pay money for on other OSes.
The modularity and flexibility of the Linux system is something I honestly forgot about and continue to be giddy about. I like having Lain-levels of control over my machine.
And games? God damn FFXIV runs better here than windows I've been scammed
38 notes
·
View notes
Note
is that the fucking fur affinity logo
It is not, though a brief internet search shows that’s not a bad guess. It is the logo for the GNOME Project, which is community that makes free and open source programs, specifically the GNOME desktop environment, for Unix-like operating systems.
On another note, if there isn’t a @fur-affinity-official or similar, someone should make it (you should. Yes I’m talking to you, the reader. Do it. Now. Let’s see who gets to it first)
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
KDE Plasma 6.3 released
Almost after a year since the first release in the sixth generation of the popular Linux and UNIX desktop environment, KDE community announces the release of the latest version of KDE Plasma 6.3 . In this major release the System Settings’ Drawing Tablet page has been overhauled and split into multiple tabs to improve how things are organized, and new configuration options have been added to each section. KWin window manager makes a stronger effort to snap things to the screen’s pixel grid, greatly reducing blurriness and visual gaps everywhere and producing sharper and crisper images. In the color department, screen colors are more accurate when using the Night Light feature both with and without ICC profiles, and KWin offers the option to choose screen color accuracy. Hardware and system monitoring and information tools have also received new features and performance optimizations. KRunner (the built-in search tool that also does conversions, calculations, definitions, graph plotting, and much more) now let you jump between categories using keyboard shortcuts. A security enhancement landing in Discover software management/app store application highlights sandboxed apps whose permissions will change after being updated. If you’re a fan of the forecasts provided by Deutcher Wetterdienst, you’re in luck: Plasma 6.3’s weather widget allows using this source for weather data. You can now configure its built-in touchpad to switch off automatically, so it doesn’t interfere with your typing. When you drag a file out of a window that’s partially below other windows, it no longer jumps to the top, potentially obscuring what you wanted to drag it into. Plasma panels can now be cloned You can also use scripting to change your panels’ opacity levels and what screen they appear on. And there’s much more. To see the full list of changes, check out the complete changelog for KDE Plasma 6.3.
#kde#kdeplasma#kde plasma#plasma#plasma 6#plasma6#desktopenvironment#desktop environment#opensource#open source#freesoftware#free software#software#linux desktop#linux#gnulinux#gnu/linux#unix#bsd#computers#technology#operatingsystems#operatingsystem#operating system#operating systems#gui#userinterface#user interface
0 notes
Text
How to Transition from Biotechnology to Bioinformatics: A Step-by-Step Guide

Biotechnology and bioinformatics are closely linked fields, but shifting from a wet lab environment to a computational approach requires strategic planning. Whether you are a student or a professional looking to make the transition, this guide will provide a step-by-step roadmap to help you navigate the shift from biotechnology to bioinformatics.
Why Transition from Biotechnology to Bioinformatics?
Bioinformatics is revolutionizing life sciences by integrating biological data with computational tools to uncover insights in genomics, proteomics, and drug discovery. The field offers diverse career opportunities in research, pharmaceuticals, healthcare, and AI-driven biological data analysis.
If you are skilled in laboratory techniques but wish to expand your expertise into data-driven biological research, bioinformatics is a rewarding career choice.
Step-by-Step Guide to Transition from Biotechnology to Bioinformatics
Step 1: Understand the Basics of Bioinformatics
Before making the switch, it’s crucial to gain a foundational understanding of bioinformatics. Here are key areas to explore:
Biological Databases – Learn about major databases like GenBank, UniProt, and Ensembl.
Genomics and Proteomics – Understand how computational methods analyze genes and proteins.
Sequence Analysis – Familiarize yourself with tools like BLAST, Clustal Omega, and FASTA.
🔹 Recommended Resources:
Online courses on Coursera, edX, or Khan Academy
Books like Bioinformatics for Dummies or Understanding Bioinformatics
Websites like NCBI, EMBL-EBI, and Expasy
Step 2: Develop Computational and Programming Skills
Bioinformatics heavily relies on coding and data analysis. You should start learning:
Python – Widely used in bioinformatics for data manipulation and analysis.
R – Great for statistical computing and visualization in genomics.
Linux/Unix – Basic command-line skills are essential for working with large datasets.
SQL – Useful for querying biological databases.
🔹 Recommended Online Courses:
Python for Bioinformatics (Udemy, DataCamp)
R for Genomics (HarvardX)
Linux Command Line Basics (Codecademy)
Step 3: Learn Bioinformatics Tools and Software
To become proficient in bioinformatics, you should practice using industry-standard tools:
Bioconductor – R-based tool for genomic data analysis.
Biopython – A powerful Python library for handling biological data.
GROMACS – Molecular dynamics simulation tool.
Rosetta – Protein modeling software.
🔹 How to Learn?
Join open-source projects on GitHub
Take part in hackathons or bioinformatics challenges on Kaggle
Explore free platforms like Galaxy Project for hands-on experience
Step 4: Work on Bioinformatics Projects
Practical experience is key. Start working on small projects such as:
✅ Analyzing gene sequences from NCBI databases ✅ Predicting protein structures using AlphaFold ✅ Visualizing genomic variations using R and Python
You can find datasets on:
NCBI GEO
1000 Genomes Project
TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas)
Create a GitHub portfolio to showcase your bioinformatics projects, as employers value practical work over theoretical knowledge.
Step 5: Gain Hands-on Experience with Internships
Many organizations and research institutes offer bioinformatics internships. Check opportunities at:
NCBI, EMBL-EBI, NIH (government research institutes)
Biotech and pharma companies (Roche, Pfizer, Illumina)
Academic research labs (Look for university-funded projects)
💡 Pro Tip: Join online bioinformatics communities like Biostars, Reddit r/bioinformatics, and SEQanswers to network and find opportunities.
Step 6: Earn a Certification or Higher Education
If you want to strengthen your credentials, consider:
🎓 Bioinformatics Certifications:
Coursera – Genomic Data Science (Johns Hopkins University)
edX – Bioinformatics MicroMasters (UMGC)
EMBO – Bioinformatics training courses
🎓 Master’s in Bioinformatics (optional but beneficial)
Top universities include Harvard, Stanford, ETH Zurich, University of Toronto
Step 7: Apply for Bioinformatics Jobs
Once you have gained enough skills and experience, start applying for bioinformatics roles such as:
Bioinformatics Analyst
Computational Biologist
Genomics Data Scientist
Machine Learning Scientist (Biotech)
💡 Where to Find Jobs?
LinkedIn, Indeed, Glassdoor
Biotech job boards (BioSpace, Science Careers)
Company career pages (Illumina, Thermo Fisher)
Final Thoughts
Transitioning from biotechnology to bioinformatics requires effort, but with the right skills and dedication, it is entirely achievable. Start with fundamental knowledge, build computational skills, and work on projects to gain practical experience.
Are you ready to make the switch? 🚀 Start today by exploring free online courses and practicing with real-world datasets!
#bioinformatics#biopractify#biotechcareers#biotechnology#biotech#aiinbiotech#machinelearning#bioinformaticstools#datascience#genomics#Biotechnology
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
i wish microsoft would learn how to separate an operating system into a shell and kernel like everyone else does. why should the ability to run windows apps be limited to people also running their desktop environment? why are there 3 different layers of settings apps? why did they see it fit to merge dos into windows? are they stupid? macos and linux both run on top of their respective command lines. does microsoft hate unix? when will someone build a kernel-only windows that gets the same treatment that a linux kernel does? i hate not being able to customize how i use my computer to my liking without abandoning all the software i use regularly. yeah i know firefox and clip studio and steam are on linux! but when will i be able to run janky .bat programs and weird 20 year old applets AND xfce? or gnome? or whatever keyboard-only bullshit a power user would want? are they stupid? i swear to god microsoft only does this shit because so many people rely on true backwards compatibility with old windows versions (some of which DID run on top of dos) and cant afford to switch. theres only so much wine or proton can do! i appreciate all the work being put into them but theyre band-aids compared to how awful windows is. maybe one day someone will find a way to rip all of the rotting layers of user experience off of what windows does on a system level and maybe itll even get an update or two. but of course who in the right mind would daily drive something like that? are you stupid? i would rather be using god damn chromeos because at least that gets fixes regularly. every venture microsoft has had into non-windows things has been pretty good! powershell is neat in how close to linux it is but youre still only half-emulating it in windows. the command prompt works as a terminal but is so crippled in functionality that the corpse of the windows vista control panel that remains in windows 10 outweighs it in actual usefulness. are they stupid? i would march up to their washington office and hold shit ransom if i werent thousands of miles away. they cant understand the principles of a version of their own product from well over 20 years ago. run windows on dos! its easy! it keeps full compatibility and let stuff like os/2 warp work! are they stupid? are they stupid?
16 notes
·
View notes